Psoriasis is an inflamed skin disease. Occurs when the immune system is not functioning. The development of the disease is divided into clear stages - appearance, development, stabilization and regression. Different levels of psoriasis differ in the appearance of spots and rashes, itching pain and extensive skin inflammation.
Why is it necessary to differentiate between the stages of development of the disease, and what are the characteristics of the course of psoriasis at the beginning of development and in the process of recovery?
Why you need to know the stages of psoriasis
The division of psoriasis into stages is used by doctors for the selection of the correct method of therapy. The complex of drugs and external agents prescribed to treat inflammation depends on the stage of disease progression. At the onset of the manifestation of the disease, general therapy is required - vitamin complexes, diet, external aseptic treatment of the rash, for example, the course of UV procedures. Also prescribed drugs that stimulate the cleansing of the intestines, blood vessels, liver. Be sure to correct your psychoemotional condition - by a neuropathologist or psychologist.
In the early stages of the disease, they do not use strong drugs that can kill the immune system, do not prescribe hormonal ointments. This medicine has a large list of side effects, so this medicine is only prescribed when it is impossible to do without the drug.
Psoriasis: treatment in the acute stage and in remission
In the event of an acute progressive illness, several multi-action medications are prescribed. Immunosuppressants and glucocorticosteroids are often used to relieve inflammation and reduce itching. External treatment is complemented by photochemical, ultrasound and laser therapy. Also, agents are prescribed for antiseptic treatment on damaged skin.
In stable conditions, they continue to take anti-inflammatory hormone drugs, gradually reducing the dose. To restore damaged skin, an ointment with a regenerating effect is prescribed.
In forgiveness - supports the body. Proper nutrition, take vitamin and mineral complexes to restore immunity.
Punctuality of treatment
The earlier treatment is started, the easier it is to handle psoriasis. Timely therapy limits the spread of skin inflammation, reduces its levels, and prevents recurrence. Since psoriasis is often mistaken for an allergic rash at an early stage, it is necessary to know the early signs so as not to miss the appearance of skin diseases.
Note: Doctors are still investigating the cause of psoriasis. But it is well known that psoriatic skin inflammation is not contagious. It should not be taken from a sick person, or an infection in the event of an injury. This is our own personal failure in the human body.
The cause of psoriasis is immune failure, which can be caused by a variety of factors. Severe stress, poisoning (including strong drugs, industrial waste, alcohol), previous infections.
Psoriasis is difficult to treat. The disease is recurrent, recurrent. And the therapy itself is symptomatic. This consists of preventing the appearance of new spots and eliminating existing itchy skin.
What level of psoriasis is mentioned early? How to distinguish early psoriasis from diathesis rash? And how will this disease develop in the future?
Psoriasis: early stages
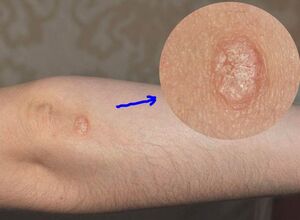
The first appearance of psoriasis on the skin looks like acne. Often, the rash appears at the elbows and knees, or in places where clothing is pressed close to the body (for example, under the belt at the waist). The rash can also appear along the edges of the hair and under the hair, around the nails and on the nail plate. Sometimes psoriasis occurs on the feet and palms.
Psoriasis almost always manifests itself symmetrically - on the elbows of both hands, or on both sides of the lower back, or on both knees. Acne itself (in medical terminology - papules) at an early stage has a moderate appearance. They have:
- Pink or red;
- Sharp and blurred edges;
- Small size - acne at the base does not exceed 2 mm;
- Flat shape - small pimples at the beginning of the disease are almost not prominent, so they look like spots.
As the disease progresses, flaky skin fragments appear on acne. They are gray or silvery, with a red acne background looking white.
The appearance of scales is accompanied by severe itching. If you do not push and scratch, the scales will be removed, displaying a shiny pink skin area underneath. It is very thin, susceptible, with prolonged itching of the itchy papules - it suffers injury, bleeding.
The early stages of psoriasis last up to 4 weeks.
Psoriasis: developmental stage
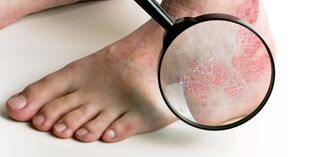
At the progressive stage, individual pimples combine into a single place, forming what are called psoriatic plaques. They are raised on the surface of the skin and completely covered with exfoliation. On the edge of the psoriatic plaque, there is a non-peeling red-pink rim.
The presence of a rim is a sign of a progressive stage of the disease. The width of the rim is 1-2 mm. The skin on it is inflamed and resembles parchment paper in the structure.
Rim represents the area of expansion of the place. This is skin that is already inflamed, but has not peeled off. After a while, it will also be covered with scales. And the patch will expand to cover new areas of skin and form wider rims.
With the active development of the disease, adjacent places merge with each other. At some point, a large, inflamed red dot can form on the human body.
Psoriatic plaques are very itchy, give an unpleasant sensation to a person, interfere with work, rest and sleep. They grow, take up large areas, and form new rashes on clean, healthy skin.
The main sign of a progressive stage is the appearance of a new rash. Once acne and new spots stop appearing, the next stage of psoriasis begins - not moving. This is not a complete victory, but it is already a recovery.
In the developmental stage, psoriasis is almost always accompanied by weakness, fatigue, weakness. Depression is common. Temperature is possible.
The duration of the progressive stage of psoriasis can be long, several months.
Psoriasis: stationary stage
The main sign of a stationary level is the cessation of the appearance of new spots and rashes. At the same time, the itching is also reduced, becoming more resistant. The rash loses bright color, changes color, becomes invisible. This is also one of the signs that the process is stable.
The pink rim around the plaque disappears when the inflammation stops spreading. Active exfoliation and healing begins, new healthy skin regrowth.
It is visible to the naked eye that exfoliation increases at a stationary level. The scales cover the entire surface of the psoriatic spot, leaving no room for rims. Psoriasis has an unknown characteristic that is often known by the general public.
Extensive peeling at a harmless stationary level. When all the dead cells come out of the surface of the psoriatic spot, healthy skin with a little light will stay in place.
Other signs of development or stabilization
In addition to the appearance of rashes, spots and scaling, there are a number of other signs that can be used to assess the progression of the disease. These are the properties of itchy sensations (strong or can withstand), general condition, depressed mood. And also the presence of temperature.
In the early stages, the itching changes, and the rash is incomprehensible. Furthermore, the itching is increasing every day. In the acute stage of psoriasis, it becomes intolerable. Disrupts sleep, rest, interferes with work. The person becomes irritable because the itchy sensation does not give him a chance to rest.
At the stationary level, the itching subsides. Every day - someone feels better. The general state of mind changes, negative and depressed mood weakens. The duration of the stationary level is a few weeks - from 2 to 5.
Psoriasis at a debilitating stage
The fading level of psoriasis is almost complete loss of plaques, spots, redness, inflammation, itching. At this stage of the disease, psoriasis is only reminiscent of different skin pigmentations. In place of former psoriatic spots, it looks lighter. A healthy skin surface has a darker color.
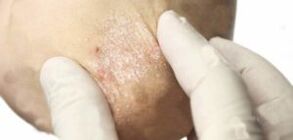
In some cases, so-called hyperpigmentation is formed. The skin at the site of psoriasis spots does not become brighter, but darker. However, skin pigmentation differences can be seen for another to two months.
Psoriasis after healing: possible recurrence
The likelihood of recurrence of psoriasis is determined by lifestyle, diet, allergic mood, and overall body condition. It is also determined by the amount of toxins in the body, blood, liver. You can reduce the chances of recurrent skin inflammation if you strengthen the immune system and cleanse the body of toxins in the liver, blood vessels, and intestines.
Seasonal psoriasis recurrence is usually rare after cleansing. A person remains prone to disease, but the chances of its occurrence are reduced.
Cleansing toxins in the body and taking vitamin and mineral complexes helps boost immunity. This is especially important if immunosuppressants are used during treatment, at a progressive stage of psoriasis. Their needs are due to the work of inflammatory mediators. After suppressing the autoimmune defense, it is necessary to restore the immune system.
Clinical manifestations
Psoriasis is characterized by monomorphic eruptions in the form of papules (nodules) of various sizes, when they merge, plaques form, and it can spread throughout the skin.
At the onset of the disease, in most cases, the rash is limited and is represented by a single plaque at its favorite localization site (scalp, extensor elbow surface, knee joint, sacrum area, etc. ).
Plaque is clearly bounded by healthy skin, bright pink or dark red, covered with loose silvery white scales, when scraped, you can acquire three characteristic features of psoriasis - "stearin spot", "terminal terminal", "blood dew ". . .
There are 3 clinical stages of psoriasis: progressive, stationary and regressive.
Classification
Depending on the stage of the inflammatory process, the localization of the dominant rash, the severity of the patient's condition, and other clinical signs, there may be plaque psoriasis, exudative, arthropathic, pustular, psoriatic erythroderma, folding psoriasis, palm and foot psoriasis. It should be noted that different clinical variants may exist simultaneously in one patient.
Exudative psoriasis is characterized by a marked inflammatory reaction on the skin, which is indicated by the presence of a lamellar scale crust on the surface of the plaque, sometimes layered, resembling a puff cake in appearance (in such cases, this form of psoriasis is called rupioid). When the crust is removed, the surface of the cry will be exposed.
Arthropathic psoriasis in the clinical picture has, in addition to the usual plaque eruption, lesions on the joints, often small, distal, less often large.
Arthropathy can occur if there are skin lesions or precursors. Psoriatic arthritis is manifested by pain, swelling, limited movement of the affected joint with varying degrees of intensity, from small arthralgias of the individual joints to lesions and deformities of the patient in general. The likelihood of arthropathic psoriasis is higher in patients with severe skin manifestations (psoriatic eroroderma, pustular psoriasis), but a combination of severe joint damage with a relatively limited skin rash is possible.
Pustular psoriasis can be generalized (Tsumbusha) and limited, with the involvement of palms and soles (Barbera). Depressive conditions, infections, irrational general or local therapy contribute to the emergence of this severe form of psoriasis.
Pustular psoriasis is common with fever, leukocytosis, increased ESR, and common serious conditions. Suddenly, against the background of bright erythema, small superficial pustules appear, accompanied by burning, pain, it can be located in the area of normal plaque and on the skin that has not previously changed. New emerging paroxysmal focal focus, occupying large areas of skin. Joint pustules cause the release of the epidermis in the form of "purulent lakes", erythrocerma can develop.
Limited pustular psoriasis is more common, rashes mainly localized on the palms and soles of the feet in the form of pustules with a background of erythema and skin infiltration. This course, compared to general, is lighter, with satisfactory general conditions, but persistent, with recurrent recurrences. Annoying local therapy is a provocative factor.
Psoriatic erythromodma is a severe form of psoriasis that develops with the gradual development of psoriatic processes and the fusion of plaque elements to the defeat of the entire skin, characterized by acute hyperemia, edema, infiltration of the skin with large and small lamellar, more rarely peelingpityriasis. Subjective - severe itching is often observed. The disease can start with erythrocerma. General conditions worsen (fever, weakness, lymph node reactions, heart failure, impaired liver and kidney function, changes in blood tests, hair loss, etc. ).
Folding psoriasis is more common in children and the elderly, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus. Lesions are located in the armpits, under the mammary glands, in the perineum, inguinal-femoral folds, in the navel and are characterized by sharp borders, saturated red color and slight exfoliation.
Psoriasis of the palms and soles of the feet may exist separately or simultaneously with lesions on other areas of the skin, characterized by the formation of hyperkeratosis foci with clear borders, covered with scars that are difficult to erase, and the presence of painful cracks. The characteristic psoriatic triad is difficult to raise.
Three clinical stages of psoriasis
Level of progress. Under the influence of provoking factors (trauma, psycho-emotional stress, infectious diseases, inadequate treatment methods, etc. ), exacerbation of the disease can develop with the emergence of abundant small nodules on peripheral growth, and the formation of plaques of various sizesand shape, which can isolate or occupy large areas of skin to universal skin lesions.
At the progressive stage, symptoms of isomorphic reactions (Kebner phenomenon) are characteristic, characterized by the fact that special psoriatic eruptions appear at the site of injury, even minor ones.
Stand still. At a stationary level, the appearance of new elements stops and the peripheral growth tendency of existing plaques disappears.
Regressive stage. The regressive stage is characterized by decreased plaque color intensity, flattening, decreased desquamation, infiltration, reabsorption of elements with subsequent hypo- or hyperpigmentation focus formation at the site of the previous rash.
Treatment
Psoriasis treatment aims to suppress the growth of epithelial cells and eliminate the inflammatory process and is prescribed taking into account the anamnestic data, form, stage, prevalence of the process, concomitant disease, age and sex of the patient, contraindications to certain treatment methods or medications.
For mild and limited manifestations of psoriasis, local external therapy in the form of salicylic ointment, naphthalan preparations, tar or emollient ointment is sufficient. Severe forms of the disease require complex systemic treatment with the use of detoxification, desensitization, anti-inflammatory drugs of different groups, methods of physiotherapy therapy, external drugs, etc.
This section will present the methods and methods of psoriasis therapy available and most modern effective.
Systemic therapy
There are specialties of managing patients at different stages of the psoriatic process. Advanced treatment requires special care. During this period, hemodez was prescribed intravenously, 30 percent. sodium thiosulfate iv solution, 10% calcium gluconate solution, with concomitant hypertension, is recommended to introduce magnesia sulfate solution; emollient cream or 1-2 percent is used externally. salicidal ointment.
Aromatic retinoid.Acitretin (neotigazone) - a representative of the second generation monoaromatic retinoid, used to treat severe psoriasis at a dose of 10 to 20-30 mg per day, depending on the severity of the skin process. The mechanism of action of acitretin is to inhibit the proliferation of epidermal cells, normalizing the keratinization process. This drug is very effective in combination with PUVA therapy. When prescribing acitretin, one should not forget its teratogenic effects.
Cytostatics.Methotrexate is used in cases of persistent psoriasis and is contraindicated in other treatment methods, as an folic acid antagonist, it acts primarily on active cell proliferation. Very toxic. There are many methods of use, preferably intramuscular administration once a week under strict laboratory control.
Immunosuppressant.Cyclosporin-A is prescribed in severe and widespread cases of psoriasis against other therapies. The drug has immunosuppressive action, has inhibitory effects on cell growth process, suppresses secretion of activated cytokine lymphocytes and receptor expression for interleukin-1 in immunocompetent cells. With psoriasis, it is prescribed at the rate of 5 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugsare prescribed for arthropathic psoriasis, as well as for the reduction of acute inflammation in exudative psoriasis and erythrocerma. The daily dose of the drug and the duration of treatment depend on the intensity of the pain syndrome, the degree of inflammation and individual tolerance.
The use of systemic corticosteroid drugs in the treatment of psoriasis is considered inappropriate, it leads to the development of forms of disease resistant to various types of therapy. In cases of severe arthropathic psoriasis, the possibility of prolonged intra-articular administration of corticosteroids, dose and duration of treatment depends on the size of the affected joint and the degree of inflammation.
Physiotherapy treatment.One of the most effective treatment methods is PUVA or photochemotherapy (PCT) therapy. PCT is a combination of the use of long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation (wavelengths from 320 to 420 nm) and photosensitive furocoumarin drugs. The use of photosensitizers is due to their ability to increase the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet rays and stimulate the formation of melanin. PUVA therapy leads to inhibition of cell proliferation, suppression of pathological keratinization, affects prostaglandin metabolism, cell membrane permeability. The peak of photosensitive effects occurs 1-3 hours after taking 8-methoxypsoralen. The dose of the drug is chosen taking into account the patient's weight. The procedure is performed 3-4 times a week, for 20-25 sessions.
Local PCT is also used with the use of external photo expansion.
The combination of use of PUVA and retinoid therapy is called Re-PUVA therapy. It has the highest clinical effect in severe cases of psoriasis.
Selective photography (SFT) - ultraviolet irradiation in medium wavelength spectrum (wavelength 280-320 nm) without taking a photo developer. SFT is used for less obvious manifestations of the disease, there are contraindications to the appointment of PUVA therapy.
How to recognize psoriasis at an early stage
Psoriasis treatment is most effective at an early stage. Therefore, it is very important to make a timely diagnosis. Only a dermatologist can tell you if you have psoriasis or any other skin disease. However, you can recognize the disease in yourself with some characteristic signs:
- Often, psoriasis first appears on the folds of the arms and legs, in the hairline or where clothing comes in close contact with the body or rub - under the pants belt, various elastic bands or straps.
- At the onset of the disease, a very severe itchy rash appears, covered with gray or silvery skin that is very easily removed.
- Removing the crust shows thin, shiny and slightly moist skin.
- If you scrape a plaque with something like a spatula, remove the scales, then blood will appear in place in the form of small drops. However, it is better not to use the latter method to self-diagnose psoriasis - it is very easy to infect the infection.
For full confidence, you need to see a doctor, as patients themselves often confuse psoriasis with various types of lichen or allergic dermatitis and use medications that are not suitable for treatment.
What to do if you find symptoms of early stage psoriasis?
Psoriasis cannot be cured forever, so the main goal of therapy is to achieve a stable and lasting remission. You should be aware that without proper treatment, psoriasis quickly becomes chronic: exacerbations can occur up to 9 times a year, lasting up to 15 days.
What to do if you suspect you have psoriasis? Often people, after knowing the signs of the disease themselves, make a big mistake, using "heavy artillery" - a hormonal ointment (called topical glucocorticosteroids, or THCS), without consulting a doctor. Usually, patients describe such a move because they allegedly heard from a friend that the fund was helping quickly. This is a big mistake!
What are the dangers of self-medication? Hormone ointment for psoriasis has many side effects and contraindications. It is highly undesirable to use it without strict doctor's recommendations regarding the duration of use, frequency, area of application on the body, and even without taking into account the individual characteristics of your body.
For effective early psoriasis treatment, non-hormonal agents such as zinc pyrithione should be used. Zinc pyrithione, or active zinc, is a very effective drug for the treatment of psoriasis, which has a complex effect:
- suppresses the proliferation and inflammation of excessive skin cells, reduces the formation of scales and the formation of psoriatic plaques;
- relieves itching;
- protects damaged skin from bacterial and fungal infections;
- restores lipid layer and skin protective function.























